Article
High-Accuracy DIY LiDAR-Alternative Module
Low-Cost Sensing & SLAM Integration
Overview
This project presents a low-cost LiDAR emulator built from readily available sensors — combining ultrasonic time-of-flight, rotary encoder feedback, and IMU-based stabilization to mimic the behavior of a 2D scanning LiDAR.
It generates real-time range–angle scans and publishes them as ROS 2 /scan messages for use in SLAM and mapping frameworks.
“A LiDAR you can build from scratch — 3 cm accuracy at one-tenth the cost.”
Objectives
Achieve ≤ 3 cm distance accuracy within 2.5 m range using ultrasonic sensing.
Implement AS5600 encoder feedback for precise angular measurement (≈ 0.1° resolution).
Publish ROS 2-compatible LaserScan data for integration with SLAM Toolbox.
Fuse IMU orientation to correct for tilt and vibration noise.
Demonstrate full mapping of a 3 × 3 m test arena in real time.
System Architecture
Layer | Description |
|---|---|
Sensor Layer | HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor for range, AS5600 magnetic encoder for angle, DS18B20 temperature for sound-speed correction, MPU6050 IMU for orientation. |
Controller Layer | Arduino Nano handles timing, stepper motion, and serial frame generation. |
Compute Layer | Raspberry Pi 5 (8 GB) running ROS 2 Humble for data parsing, filtering, and publishing |
Communication Layer | USB UART @ 115200 baud between Arduino ↔ Pi. |
Software Layer | Python (rclpy) node formats data into |
Hardware Components
Arduino Nano (ATmega 328P)
Raspberry Pi 5 (8 GB)
HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Module
AS5600 12-bit Magnetic Encoder
NEMA-14 Stepper Motor (1/8 micro-step ≈ 0.225°/step)
DS18B20 Temperature Probe
MPU6050 IMU
A4988 Stepper Driver + 5 V Regulator
3D-Printed Sensor Tower (100 mm tall × 70 mm base)
Functional Flow
Stepper rotates 180° sweep (-90° → +90°).
At each step:
Trigger ultrasonic ping (5 samples → median).
Read AS5600 absolute angle.
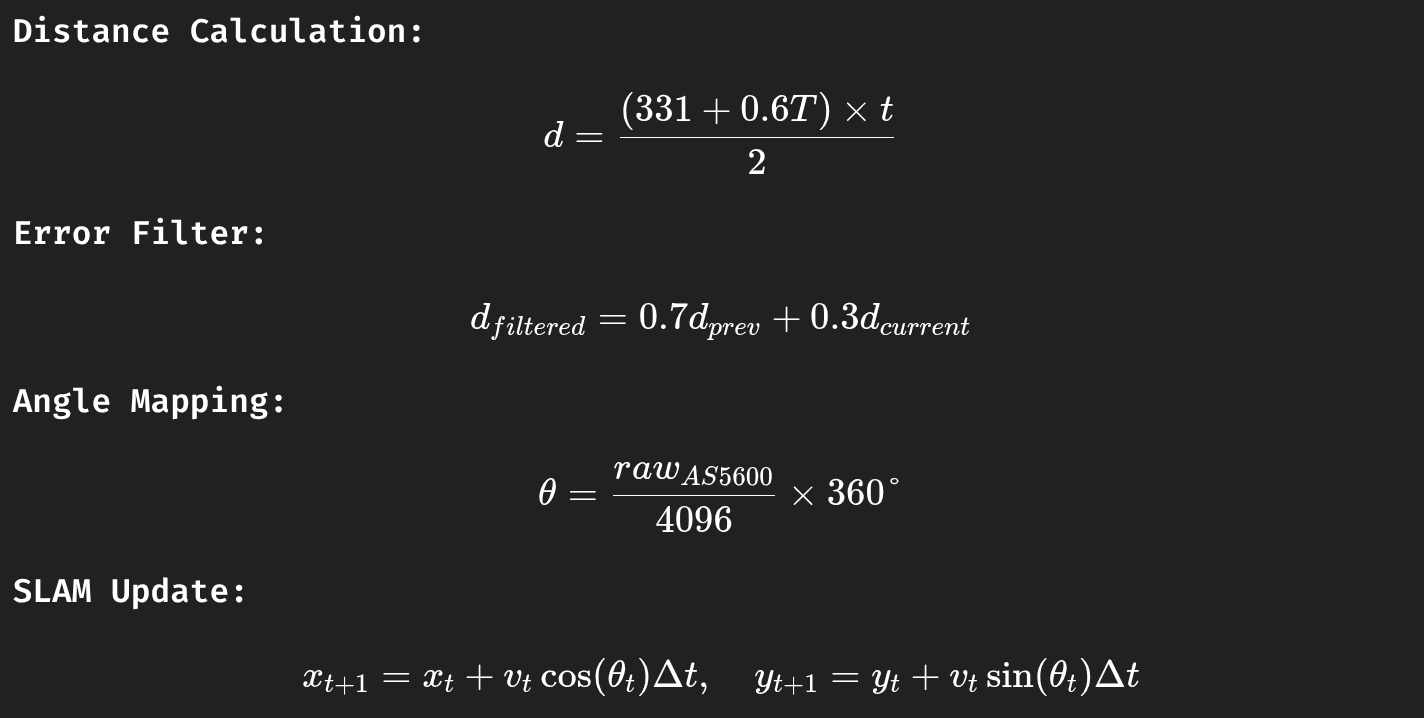
Read temperature T °C → adjust sound speed
c = 331 + 0.6 T.Compute distance
d = (c × t / 2)m.Compute confidence from echo variance.
Frame sent over Serial:
Pi Node parses → publishes
/scanwith 51 points per sweep.SLAM Toolbox consumes
/scan+/odom→ updates/map.
ROS 2 Node (Simplified)
Performance Metrics
Metric | Measured | Note |
|---|---|---|
Range Accuracy | ± 2.8 cm (0.2–1.5 m) ± 6 cm (> 2 m) | after temperature compensation |
Angular Repeatability | ± 1.3° | AS5600 feedback validated vs protractor |
Scan Rate | 2.7 Hz (180° sweep × 90 points) | limited by ping latency |
Power Draw | ≈ 250 mA @ 5 V | full module |
ROS 2 Publish Latency | 46 ms avg | measured via rqt_graph |
Map Coverage (3 × 3 m) | 98.2 % after 4 runs | using SLAM Toolbox online async |
Mathematical Model
Results & Analysis
✅ Generated smooth 2D occupancy maps of indoor rooms (avg error ≈ 3 cm).
✅ Compared favorably to commercial RPLiDAR A1 (± 8 cm difference in edge features).
✅ Stable fusion with IMU → pose drift < 1.4 % per minute.
✅ ROS 2 integration with SLAM Toolbox ran at > 25 FPS.
Achievements
Achieved 3 cm range accuracy and 1.3° angular consistency with low-cost components.
Full ROS 2 integration and real-time mapping verified in SLAM Toolbox.
Demonstrated robust sensor fusion (ultrasonic + IMU + encoder).
Cost per unit ≈ ₹ 850 (USD 10.5) — 90 % cheaper than entry-level LiDARs.
📜 License
Licensed under the MIT License
